Mekkit University 033 Path Layering (Features)
Hey everyone!
Path layering is the process of placing multiple paths on the same tile. This has many different effects that alter the aesthetic and the guests' behavior! This is the second part, taken from Mekkit's Path Layering Compendium.
Path Layering Features
Cool and useful tricks done with path layering
Path over Queues:
Queue lines can be upgraded with path layering, replacing the bright plastic vanilla queues with normal path textures. The white queue handrails can be optionally kept, or hidden with a corrupted element to make room for other, less bright handrails. Copy and paste corners and straight path sections over the top of queues.

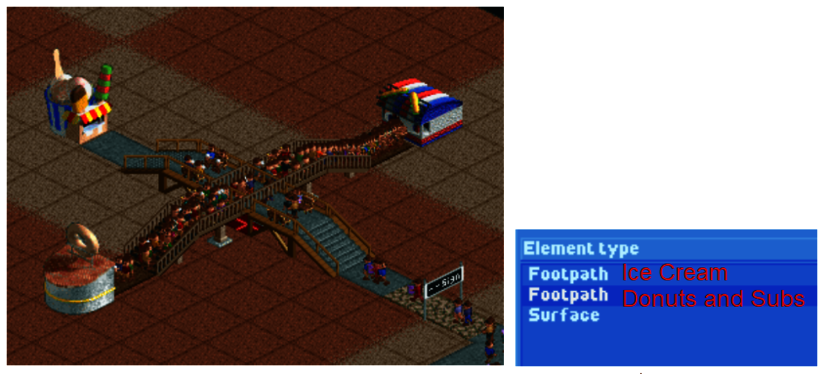
Crossing Paths:
Less of a feature and more of an observation. When two separate pathways overlap on a tile, the guests will treat it as a junction and will prefer the lower order path, only staying on the high level path to continue walking straight. Guests cannot walk onto the higher order path from the lower order path. Once they are walking on the lower order path, they may not leave that path. (Here, most guests immediately turned off the grey path to grab some donuts and subs. A few guests chose to stay on the grey path and grab some ice cream. Once on the brown path, these guests cannot find the grey path again to leave.)
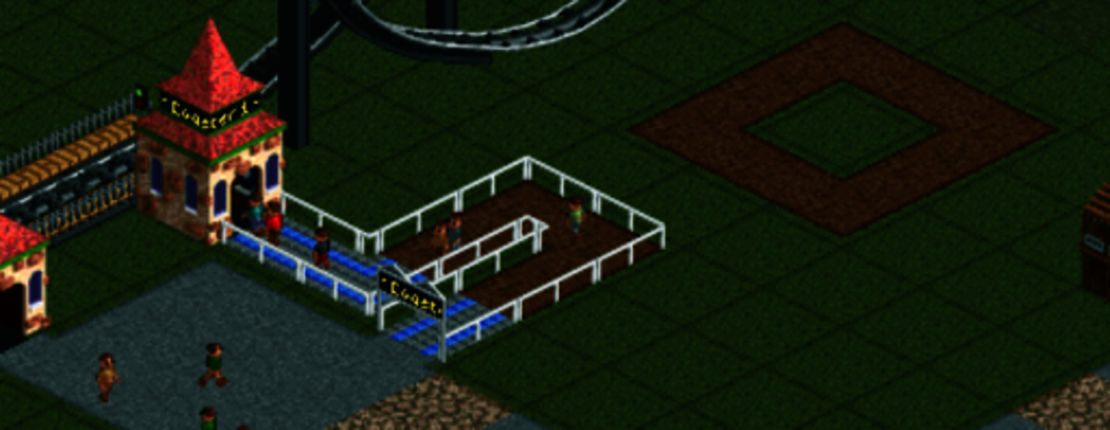
Path over Park Entrance:
The middle section of a Park Entrance counts as a path while path layering. Copy and paste a path section over the entrance. Be sure to keep this Park Entrance piece ordered below all other paths, otherwise the guests will not be able to use the entrance to enter or exit the park.

Diagonal Paths:
Path layering can be used to fill the gaps between path and block to make seamless diagonal paths. Hide the normal path with corrupted elements and copy paste a fulltile path over the top.

Railings:
Path layering can be used to combine different path railing types. All railings will be drawn, but some railings are bulky enough to hide the smaller railings.

Supports:
Path layering can be used to combine different path support types. The lowest ordered path will keep its supports. All higher ordered paths will have their supports hidden.

Seating Areas:
Path layering can be used to fill pavement gaps in benched seating areas.

Proxy Paths:
Path layering can be used to hide a narrow guide path underneath a much larger path area to force guests to walk where we want them. Particularly useful for extra wide paths and for large, open plazas.

Added Texture:
Layer unconnected path squares over wide paths to add texture.